

Create a state diagram for the required sequential circuit with the desired output states.Steps of Sequential logic circuit design: So for creating a static memory cell in the circuit, we use inverters. And for the memory element, we need a static memory element to store data in circuitry. We already know that a sequential logic circuit combines the combinational circuit with a memory element. Sequential logic circuit design | Sequential logic design principles Here the arrow starts with one circle and goes to another circle and sometimes it can come back to the same circle depending upon the condition. When there is pulse output the arrow can be represented with the output related to the input pulse. In this type of diagram that state is mainly represented as a circle and the change from one state to another is denoted by an arrow, along with that arrow the input pulse is represented, which causing the transition between the state. Sequence logic state diagram is a characteristic diagram of the circuit, in which we can determine the transition between the states concerning the input. State output is always predictable State output sometimes unpredictable This circuit consumes somewhat high power. Relatively faster working than that of the synchronous sequential logic circuit.

Relatively slower than that of an asynchronous sequential logic circuit. The output of this logic circuit only depends on the input pulse and the sequence of previous input data. Difference between synchronous and asynchronous sequential logic circuits: Synchronous sequential logic circuit Asynchronous Sequential logic circuit The output of this logic circuit depends upon the input pulse as well as the clock pulse of the circuit. Forming this type of circuit is also difficult.
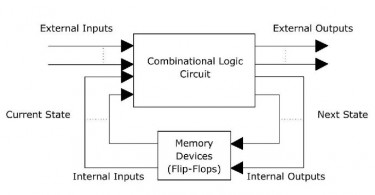
Because of the asynchronous behaviour, the output sometimes may be uncertain, limting the application of the asynchronous sequential logic circuit. These circuits are mainly used when the speed of operation is a priority, such as in microprocessors, digital signal processing, for internet access, etc. It consumes less power, low electromagnetic interference.Īsynchronous sequential logic circuits usually perform operations in following cases : The only hindrance to the speed of this circuit is the propagation delay of the circuit elements. The output of this logic circuit only depends on the input pulse and the sequence of previous input data, This circuit doesn’t have any clock and doesn’t need any synchronization, so the circuit is independent of the clock, which makes it faster than the synchronous sequential logic circuit because the output can change concerning change in input with minimum time required can be affected regardless of time. Example of the synchronous logic circuits is flip-flops, synchronous counter, etc. So for a properly working circuit, we need a definite time interval so that all elements can get their time to respond properly. The propagation delay can vary from element to element. There is a need for a finite amount of time for the processed output to occur mainly, known as propagation delay. This type of circuit may be used to synchronize all the elements present in the circuit, practically for responding to a change in input. For a change in one state output to another, this circuit waits for the next change in clock pulse. Without any clock pulse, there will be no change in output. Here memory element and the clock is a necessity. the output can change only after a finite interval of time. The circuit is synchronized with the clock, i. The output of this logic circuit depends upon the input pulse and the clock pulse of the circuit. Generally, we can differentiate the sequential logic circuit into two basic types: Sequential Logic Circuit Types of sequential logic circuits: Sequential Logic Diagram | Sequential Logic Architecture : Fig. A sequential logic circuit is mainly used as a register, counter, analog to digital converter (ADC), etc. Due to the memory element, this circuit provides the solution to our many problems. This type of circuit has a finite number of inputs with a finite number of outputs. The memory element in the circuit can store one bit at a time. At the same time, the sequential logic circuit is generally known as a two-state or bistable device because it has only two stable states, ‘0’ and ‘1’, one state at a time. With the presence of a memory element, the circuit can store previous input and output states.
The sequential logic circuit is a combined form of the combinational circuit with a basic memory element. Content: Sequential Logic Sequential logic definition:Ī type of logic in which the previous sequence state of inputs as well as current input can affect the present output state.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
